Thick and highly conductive
Copper in printed circuit boards is used to transmit electrical current and signals. As power semiconductors become more and more powerful, there are power applications where a lot of current or voltage has to be switched and where correspondingly special solutions with copper are needed for current and voltage management as well as for heat dissipation.
For these applications, thicker copper is required. Standard copper layer thicknesses in printed circuit boards are normally between 18 and 35 µm and in special cases up to 70 µm. Printed circuit boards with more than 70 µm final copper are called thick copper printed circuit boards (heavy copper). The thick copper layers can be designed as both outer and inner layers.
The challenge for the production of such PCBs lies in the uniform etching pattern, the dielectric separation of the layers in the multilayer and the insulation of the conductive tracks. Another challenge is the application of solder resist that covers the entire surface. Prepregs must be selected so that suitable glass types and resin contents are used. The lamination conditions must also be adapted.
We have experience in the production of thick copper printed circuit boards -also as high layer design. For up to 204 µm copper inner or outer layer, our Chinese fabrications can show UL approval (E229342).
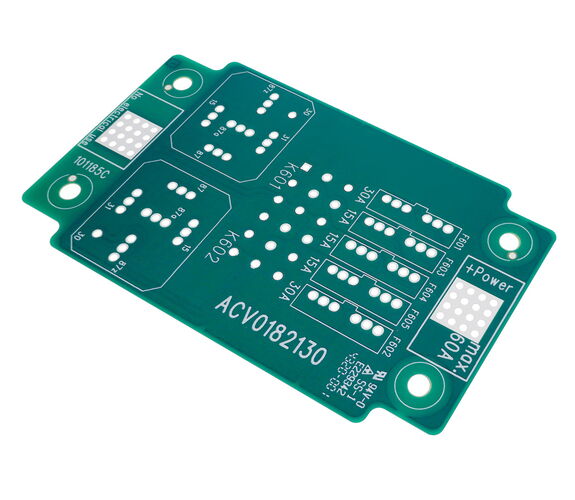
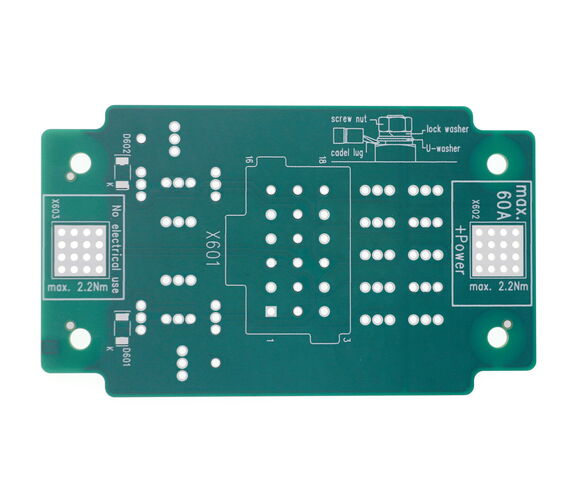
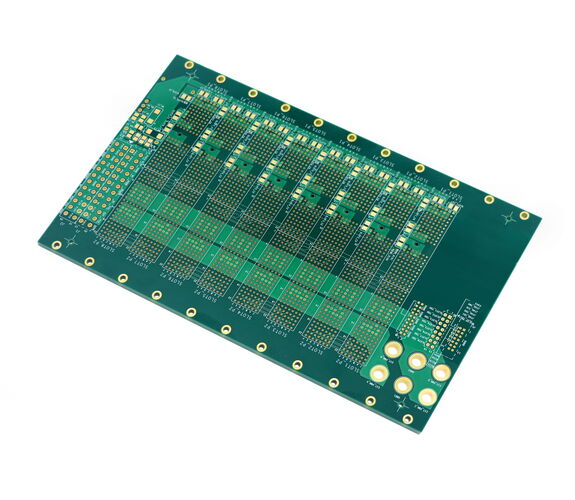
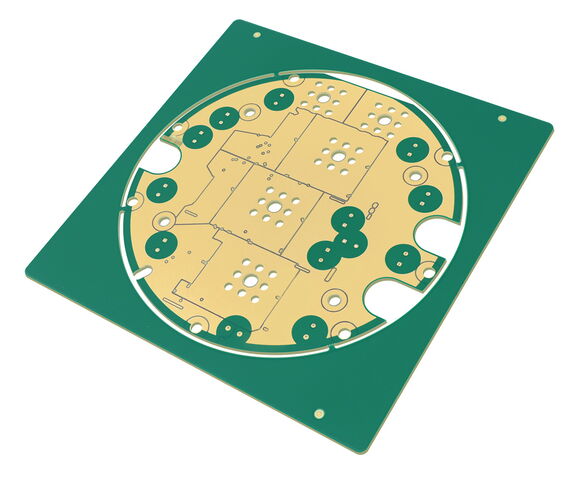
Advantages:
- Ideal for higher currents / increase in current flow capacity.
- Conduction of high currents
- Combination of signal and power layers on one PCB
- Combination with HDI and Semiflex
- Standardized assembly and mounting
Technology spectrum
- 105 to 210 µm copper
- 2 to 26 layers
- Blind and buried vias possible
Application examples
- Devices with continuous current up to over 200 amps
- Relay and fuse boxes, DC/DC converters
- Power supply
- Power distributors
- Electric drive technology and motor control
- Planar transformers
- Inverters and frequency converters
- Power and energy management
- Signaling technology

